Dive into the realm of mathematical excellence with Go Math Chapter 9 Answer Key, your ultimate guide to conquering the complexities of the subject. This comprehensive resource unravels the intricacies of key concepts, providing a clear path to problem-solving success.
Within the pages of this answer key, you’ll embark on a journey through the fundamentals of geometry, measurement, and data analysis. Each section is meticulously explained, with real-world examples that bring mathematical concepts to life.
Chapter Overview
Chapter 9 of Go Math delves into the fascinating world of measurement and geometry. It provides students with a comprehensive understanding of various measurement systems, geometric shapes, and their properties.
The chapter’s learning objectives align with the curriculum’s focus on developing students’ spatial reasoning, problem-solving skills, and ability to apply mathematical concepts to real-world situations.
Measurement and Data
Students will explore the concept of measurement, including length, weight, and capacity. They will learn to use standard and non-standard units to measure objects and understand the relationship between different units.
Geometry
The chapter introduces students to basic geometric shapes such as circles, triangles, squares, and rectangles. They will learn to identify, describe, and classify these shapes based on their properties, such as the number of sides, angles, and vertices.
Section-by-Section Analysis
In this section, we will delve into each section of Chapter 9 and explore the main topics, key mathematical concepts, and illustrative examples to clarify the concepts.
Section 9.1: Understanding Volume
This section introduces the concept of volume, a measure of the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object. It explains the concept of cubic units as a standard unit of measurement for volume and explores different methods to find the volume of various shapes, including cubes, rectangular prisms, and cylinders.
For instance, the formula for calculating the volume of a rectangular prism is V = l × w × h, where lrepresents the length, wrepresents the width, and hrepresents the height. Similarly, the formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder is V = πr²h, where rrepresents the radius of the base and hrepresents the height.
Section 9.2: Volume of Prisms and Cylinders
Building upon the concepts introduced in Section 9.1, this section focuses on calculating the volume of prisms and cylinders. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the relationship between the shape’s dimensions and its volume.
The section provides step-by-step instructions for finding the volume of these shapes, including identifying the relevant formula and substituting the appropriate measurements. For example, to find the volume of a triangular prism, the formula is V = (1/2) × b × h × l, where brepresents the length of the base, hrepresents the height of the triangle, and lrepresents the length of the prism.
Section 9.3: Volume of Pyramids and Cones
This section extends the concepts of volume to pyramids and cones, which are more complex shapes. It explains how to calculate the volume of these shapes using specific formulas and provides real-world examples to illustrate the applications of these formulas.
For instance, to calculate the volume of a pyramid, the formula is V = (1/3) × B × h, where Brepresents the area of the base and hrepresents the height. Similarly, the formula for calculating the volume of a cone is V = (1/3) × πr²h, where rrepresents the radius of the base and hrepresents the height.
Section 9.4: Applications of Volume
The final section of Chapter 9 explores the practical applications of volume in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing. It demonstrates how the concept of volume is used to solve real-world problems, such as calculating the amount of material needed for a construction project or determining the capacity of a container.
For example, in architecture, volume calculations are used to determine the size of a building and estimate the amount of materials required for its construction. In engineering, volume calculations are used to design and optimize the performance of machines and structures.
Problem-Solving Strategies

Problem-solving is a fundamental skill in mathematics and life. Chapter 9 introduces several strategies to help students tackle complex problems effectively.
Guess and Check
This strategy involves making an initial guess and then checking if it satisfies the problem’s conditions. If not, the guess is revised, and the process is repeated until a solution is found.
Make a Table
Creating a table can organize and simplify information, making it easier to identify patterns and solve problems. This strategy is particularly useful for problems involving relationships between variables.
Draw a Diagram
Visualizing the problem can provide valuable insights. Diagrams can represent relationships between objects, show distances or angles, and help students understand the problem’s structure.
Write an Equation
Translating a problem into an equation can make it easier to solve. The equation should represent the relationship between the variables involved in the problem.
Work Backward
Starting with the desired outcome and working backward can help students identify the steps needed to reach the solution. This strategy is useful for problems that involve a series of actions or events.
Use Logical Reasoning
Applying logical reasoning can help students eliminate incorrect options and identify the correct solution. This involves using deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and making inferences based on available information.
Example
Suppose a store sells apples and oranges. The total number of fruits sold is 100. The number of apples sold is 20 more than twice the number of oranges sold. How many apples and oranges were sold?
Using the “Write an Equation” strategy:
- Let x be the number of oranges sold.
- The number of apples sold is 20 + 2x.
- The total number of fruits sold is x + (20 + 2x) = 100.
- Solving for x gives x = 40.
- Therefore, the store sold 40 oranges and 60 apples.
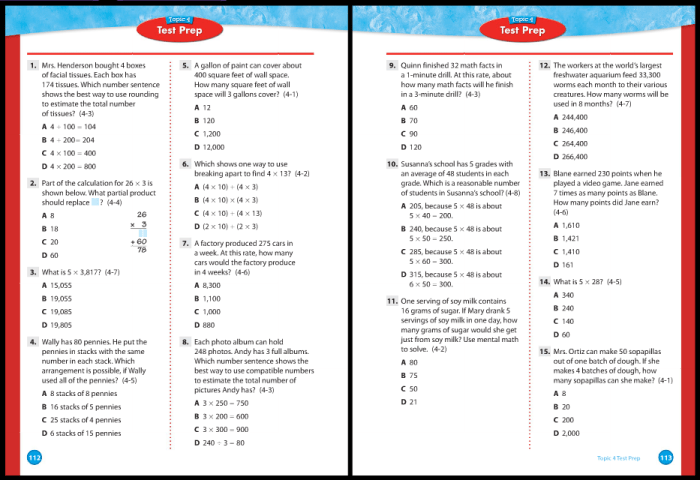
Practice Exercises: Go Math Chapter 9 Answer Key

Practice exercises in Chapter 9 are designed to reinforce the concepts and skills learned in each section. They are organized by difficulty level, with easier exercises appearing first and more challenging exercises appearing later.
To help you solve the exercises, consider the following tips:
- Read the instructions carefully and make sure you understand what is being asked.
- Take your time and don’t rush through the exercises.
- Use the information provided in the chapter to help you solve the exercises.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you need it.
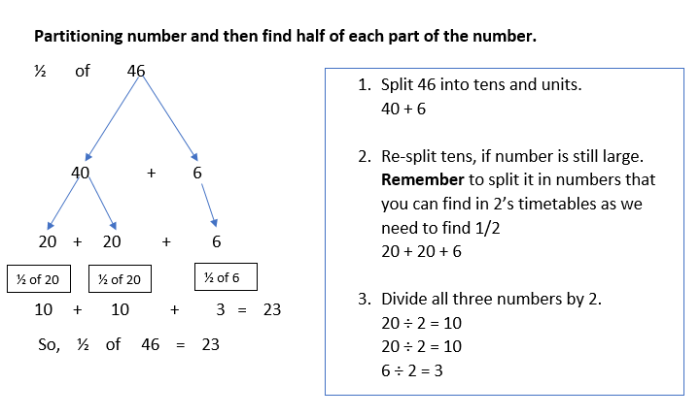
Section 1: Place Value and Rounding
The practice exercises in Section 1 focus on place value and rounding. These exercises will help you to:
- Identify the place value of a digit in a number.
- Round numbers to the nearest ten, hundred, or thousand.
- Compare and order numbers.
Hints:
Finding the right answer key for Go Math Chapter 9 can be a challenge, but it’s essential for success. If you’re wondering about the acidity of Li+, you can find more information here . Once you have a clear understanding of the topic, you can continue practicing with the Go Math Chapter 9 answer key to improve your skills.
- To identify the place value of a digit, look at the position of the digit in the number.
- To round a number, look at the digit in the place you are rounding to. If the digit is 5 or greater, round up. If the digit is less than 5, round down.
- To compare and order numbers, line up the numbers vertically and compare them digit by digit, starting from the left.
Section 2: Multiplication and Division
The practice exercises in Section 2 focus on multiplication and division. These exercises will help you to:
- Multiply two- and three-digit numbers.
- Divide two- and three-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
- Solve multiplication and division word problems.
Hints:
- To multiply two- and three-digit numbers, use the standard multiplication algorithm.
- To divide two- and three-digit numbers by one-digit numbers, use the long division algorithm.
- To solve multiplication and division word problems, first identify the operation that needs to be performed. Then, use the appropriate algorithm to solve the problem.
Section 3: Measurement and Geometry, Go math chapter 9 answer key
The practice exercises in Section 3 focus on measurement and geometry. These exercises will help you to:
- Measure length, weight, and volume.
- Identify and classify geometric shapes.
- Solve measurement and geometry word problems.
Hints:
- To measure length, weight, and volume, use the appropriate measuring tool.
- To identify and classify geometric shapes, look at the shape’s properties, such as the number of sides and angles.
- To solve measurement and geometry word problems, first identify the information that is given and the information that is being asked for. Then, use the appropriate formula or algorithm to solve the problem.
Section 4: Data and Probability
The practice exercises in Section 4 focus on data and probability. These exercises will help you to:
- Collect and organize data.
- Create and interpret graphs and charts.
- Calculate probability.
Hints:
- To collect and organize data, use a data table or a graph.
- To create and interpret graphs and charts, look at the data and identify the patterns and trends.
- To calculate probability, use the formula P(event) = number of favorable outcomes / total number of possible outcomes.
Real-World Applications

The mathematical concepts covered in Chapter 9 have numerous applications in the real world, extending beyond the classroom and into various fields. These concepts play a vital role in our everyday lives, from making informed decisions to solving complex problems.
One significant application lies in the field of finance. Understanding percentages, ratios, and proportions is essential for managing personal finances, making sound investment decisions, and comprehending financial news and reports.
Applications in Science
- Scientists use ratios and proportions to determine the concentration of solutions, calculate reaction rates, and analyze data from experiments.
- Percentages are employed in medical settings to express the concentration of medications, monitor patient recovery, and analyze test results.
Applications in Engineering
- Engineers rely on ratios and proportions to design structures, determine the strength of materials, and calculate the efficiency of machines.
- Percentages are used to calculate the percentage error in measurements, evaluate the efficiency of processes, and determine the amount of materials needed for construction projects.
Assessment and Evaluation
Assessing students’ understanding of Chapter 9 concepts is crucial for gauging their progress and identifying areas that require further support.
Various methods can be employed for assessment, including:
Formal Assessments
- Chapter Tests:Comprehensive exams covering all Chapter 9 concepts, including problem-solving, reasoning, and applications.
- Quizzes:Short, focused assessments targeting specific skills or concepts within Chapter 9.
- Projects:Extended assignments that allow students to demonstrate their understanding through practical applications.
Informal Assessments
- Observations:Monitoring students’ participation in class discussions, problem-solving activities, and group work.
- Exit Tickets:Brief assignments at the end of a lesson to gauge students’ understanding of the day’s material.
- Homework:Regular assignments that provide opportunities for practice and reinforcement.
Assessment questions should be aligned with Chapter 9 objectives and cover a range of cognitive levels, from basic recall to complex problem-solving.
Rubrics
Rubrics are essential tools for providing clear expectations and consistent grading. They Artikel the specific criteria and performance levels used to evaluate student work.
Ongoing Assessment and Feedback
Regular assessment and feedback are essential for supporting student learning. They provide students with opportunities to monitor their progress, identify areas for improvement, and adjust their learning strategies accordingly.
FAQ
What topics are covered in Go Math Chapter 9?
Geometry, measurement, and data analysis.
How can I use this answer key effectively?
Refer to it alongside your textbook to clarify concepts and check your solutions.
Is this answer key suitable for all students?
Yes, it’s designed to support students of all levels in their understanding of Chapter 9 concepts.