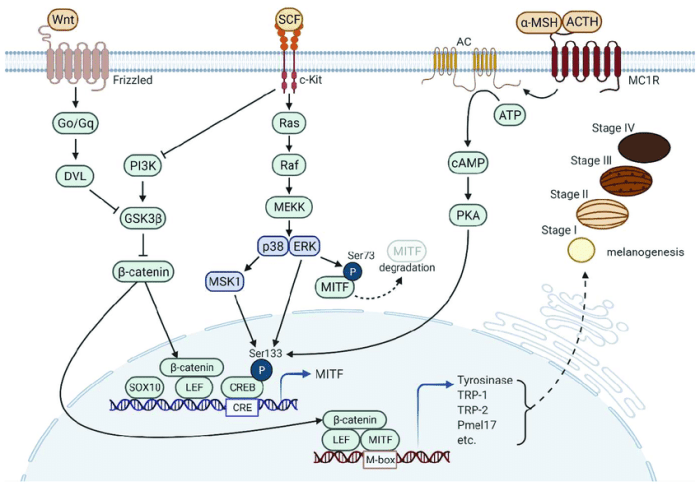
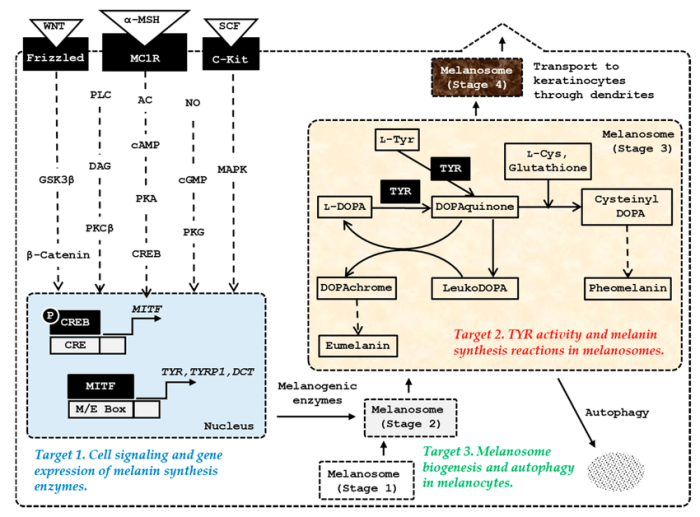
The biochemistry and cell signaling pathway of mc1r answers – Unveiling the biochemistry and cell signaling pathway of MC1R, this exploration delves into the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular responses. MC1R, a pivotal G protein-coupled receptor, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including skin pigmentation and immune function.
Understanding its signaling pathway is essential for deciphering the molecular basis of these processes and identifying potential therapeutic targets.
Delving into the biochemistry of MC1R, we examine its structure, ligand binding properties, and post-translational modifications. The cell signaling pathway activated by MC1R involves G protein coupling, second messenger activation, and downstream effector engagement. We explore the regulation of MC1R signaling, including mechanisms controlling its expression, phosphorylation, and the impact of mutations.
Introduction
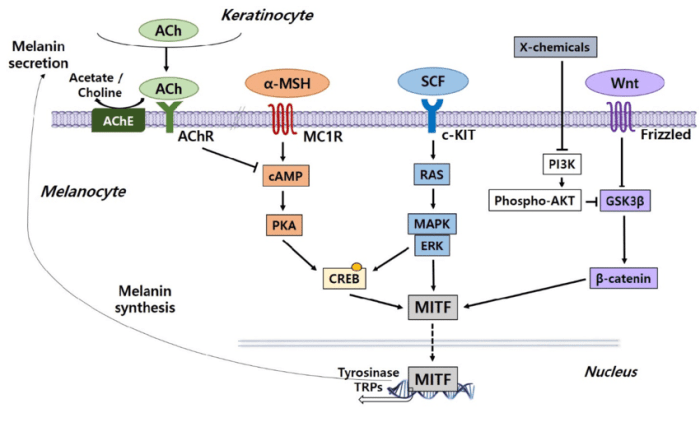
The melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that plays a critical role in cell signaling and pigmentation. Understanding the biochemistry and cell signaling pathway of MC1R is essential for elucidating its physiological functions and potential therapeutic applications.
Biochemistry of MC1R: The Biochemistry And Cell Signaling Pathway Of Mc1r Answers
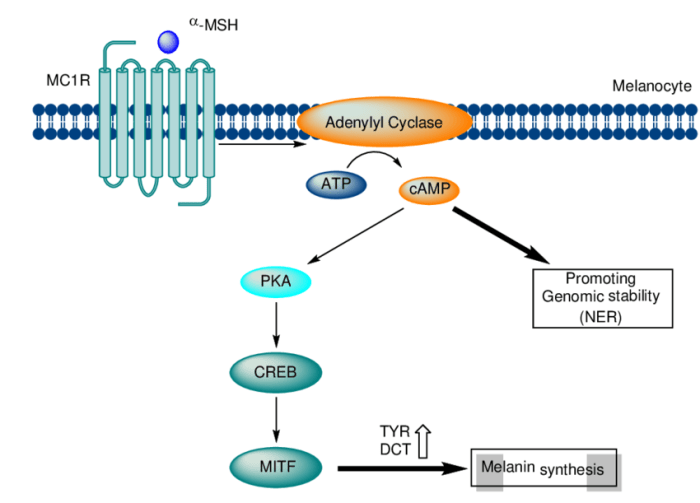
MC1R is a seven-transmembrane protein with an extracellular N-terminus and an intracellular C-terminus. The extracellular domain binds to melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), which activates the receptor and initiates intracellular signaling.
MC1R undergoes post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation and glycosylation, which modulate its function and trafficking.
Cell Signaling Pathway of MC1R, The biochemistry and cell signaling pathway of mc1r answers
MC1R activates the G protein Gs, which in turn stimulates adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular cAMP levels. cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates various downstream targets, leading to changes in gene expression and cellular responses.
MC1R signaling also involves the activation of phospholipase C (PLC), which hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to produce inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 releases calcium from intracellular stores, while DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC).
Regulation of MC1R Signaling
MC1R expression is regulated by various factors, including hormones, cytokines, and transcription factors. Phosphorylation of MC1R by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) desensitizes the receptor and terminates signaling.
Mutations in MC1R can lead to constitutive activation or impaired signaling, resulting in abnormal pigmentation and other disorders.
Clinical Significance of MC1R Signaling
MC1R plays a crucial role in skin pigmentation, with variants associated with different skin colors and susceptibility to skin cancer. Targeting MC1R signaling has therapeutic potential for treating skin disorders, such as vitiligo and melanoma.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of MC1R in skin pigmentation?
MC1R plays a crucial role in determining skin color by regulating the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin pigmentation.
How does MC1R signaling contribute to skin cancer development?
Mutations in MC1R can lead to constitutive activation of the receptor, promoting excessive melanin production and increasing the risk of skin cancer, particularly melanoma.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of targeting MC1R signaling?
Targeting MC1R signaling holds promise for treating skin cancer, vitiligo, and other pigmentation disorders by modulating melanin production and immune responses.