Label the reproductive structures of the female pelvis. – Label the reproductive structures of the female pelvis is a captivating exploration of the intricate anatomy of the female reproductive system, providing an in-depth understanding of its structures and functions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the major reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina, examining their location, functions, and clinical significance.
Overview of the Female Pelvis
The female pelvis is a bony structure located in the lower abdomen. It is bounded by the sacrum and coccyx posteriorly, the two hip bones laterally, and the pubic bones anteriorly. The female pelvis is wider and shallower than the male pelvis, and it is adapted for childbirth.
The bony structures that form the pelvis include the sacrum, coccyx, hip bones, and pubic bones. The sacrum is a triangular bone that forms the posterior wall of the pelvis. The coccyx is a small bone that is attached to the sacrum and forms the tip of the pelvis.
The hip bones are large, flat bones that form the lateral walls of the pelvis. The pubic bones are two small bones that form the anterior wall of the pelvis.

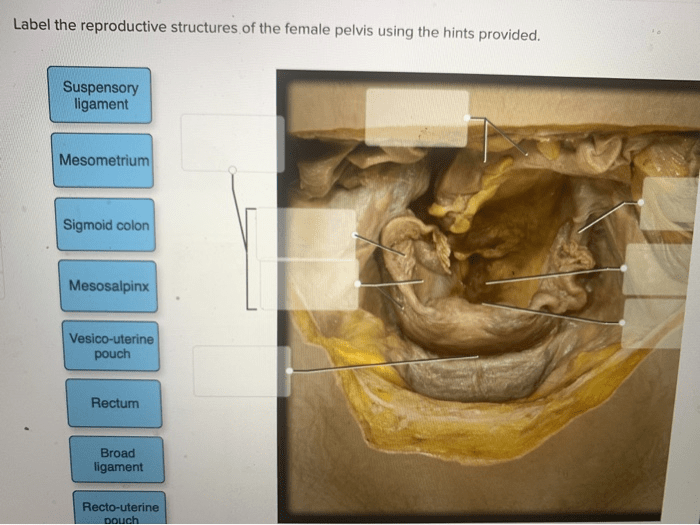
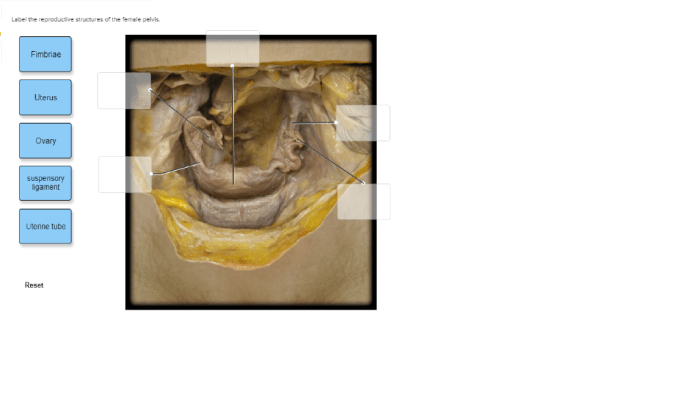
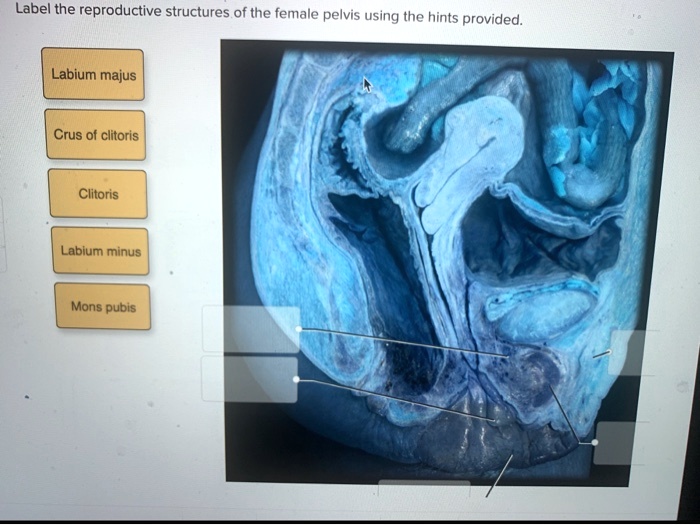
Reproductive Structures of the Female Pelvis
The major reproductive structures located within the female pelvis include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina.
| Structure | Location | Function | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uterus | In the center of the pelvis, behind the bladder and in front of the rectum | To nurture and nourish a developing fetus during pregnancy | Uterine fibroids, endometriosis, uterine prolapse |
| Ovaries | On either side of the uterus | To produce and release eggs (ova) | Ovarian cysts, ovarian cancer, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) |
| Fallopian tubes | Extend from the ovaries to the uterus | To transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus | Ectopic pregnancy, tubal ligation |
| Vagina | From the uterus to the outside of the body | To receive the penis during sexual intercourse and to allow for the passage of menstrual blood and childbirth | Vaginal infections, vaginal prolapse, vaginal cancer |
Blood Supply and Innervation of the Female Pelvis
The female pelvis is supplied by the internal iliac artery and vein. The internal iliac artery branches into several smaller arteries that supply the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina. The internal iliac vein drains blood from the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina.
The female pelvis is innervated by the pudendal nerve and the pelvic splanchnic nerves. The pudendal nerve supplies sensation to the external genitalia and the perineum. The pelvic splanchnic nerves supply sensation to the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina.

Understanding the blood supply and innervation of the female pelvis is important for a number of reasons. First, it is necessary for understanding the spread of pelvic pain. Second, it is important for planning surgical procedures in the pelvis. Third, it is important for understanding the effects of pelvic trauma.
Clinical Applications: Label The Reproductive Structures Of The Female Pelvis.
Knowledge of the female pelvis is applied in clinical practice in a number of ways. For example, it is used to diagnose and treat pelvic pain, pelvic infections, and pelvic tumors. It is also used to plan and perform surgical procedures in the pelvis, such as hysterectomy, oophorectomy, and tubal ligation.
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and MRI, are often used to diagnose and treat pelvic disorders. Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of the pelvis. MRI is a more invasive imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of the pelvis.
These imaging techniques can be used to diagnose a variety of pelvic disorders, such as uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, and pelvic tumors.
Surgical procedures are sometimes necessary to treat pelvic disorders. Hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus. Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both ovaries. Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure to block the fallopian tubes, which prevents pregnancy.
Popular Questions
What are the major reproductive structures of the female pelvis?
The major reproductive structures of the female pelvis include the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and vagina.
What is the function of the uterus?
The uterus is the site of fetal development and provides nourishment to the developing fetus.
Where are the ovaries located?
The ovaries are located on either side of the uterus.