Scatter plots and association answer key: a gateway to deciphering the intricate relationships between variables, unveiling patterns, and extracting meaningful insights from data. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of scatter plots, empowering you with the knowledge and tools to interpret, analyze, and leverage this powerful visualization technique.
Scatter plots, with their ability to reveal correlations and associations, are indispensable tools in various fields, from science and medicine to business and finance. By understanding the concepts of scatter plots and association, you gain the ability to make informed decisions based on data-driven evidence.
1. Scatter Plots
Introduction
A scatter plot is a type of graph that displays the relationship between two numerical variables. It consists of a horizontal axis (x-axis) and a vertical axis (y-axis), with each point on the graph representing a pair of data values.
Scatter plots are commonly used to visualize the relationship between two variables in various fields, such as science, medicine, and business. They can help identify trends, patterns, and correlations between different variables.
However, it’s important to note that scatter plots have limitations. They can only show the relationship between two variables at a time, and they do not necessarily imply causation.
2. Interpreting Scatter Plots

Types of Relationships
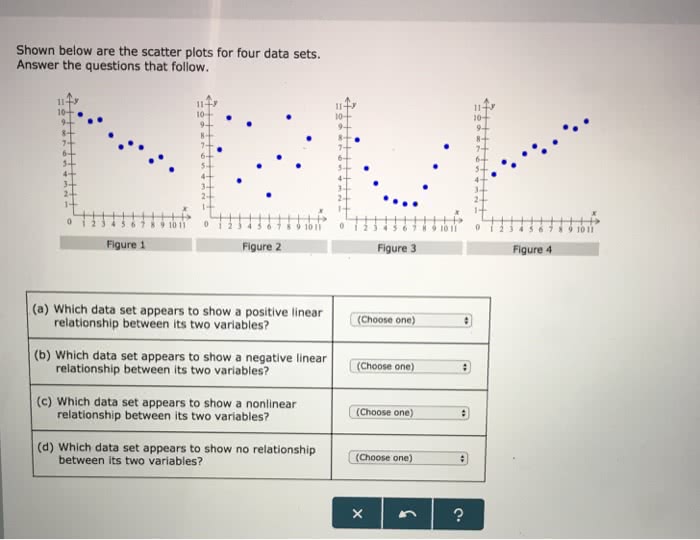
- Positive correlation: Points form a generally upward-sloping pattern, indicating that as one variable increases, the other variable tends to increase as well.
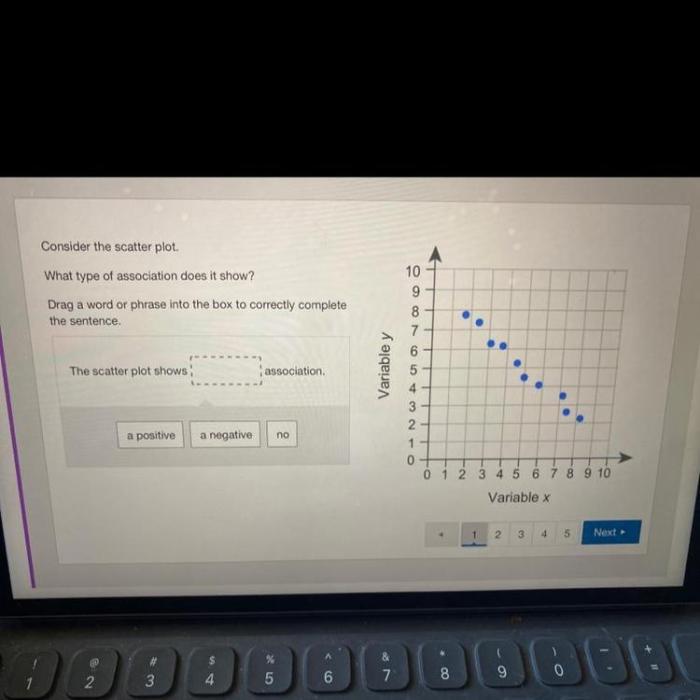
- Negative correlation: Points form a generally downward-sloping pattern, indicating that as one variable increases, the other variable tends to decrease.
- No correlation: Points are randomly scattered, indicating no apparent relationship between the variables.
Outliers, Scatter plots and association answer key
Outliers are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data. They can skew the interpretation of the scatter plot and should be carefully considered.
Context and Domain Knowledge
When interpreting scatter plots, it’s crucial to consider the context and domain knowledge. The relationship between variables may vary depending on the specific context and background information.
3. Association in Scatter Plots
Concept of Association
Association in scatter plots refers to the degree to which two variables are related. It can be quantified using measures such as correlation coefficient and slope.
Correlation Coefficient
The correlation coefficient is a statistical measure that ranges from -1 to 1. A value close to 1 indicates a strong positive correlation, while a value close to -1 indicates a strong negative correlation. A value close to 0 indicates no correlation.
Slope
The slope of a linear regression line fitted to the data points in a scatter plot represents the change in the y-variable for each unit change in the x-variable.
Correlation vs. Causation
It’s important to distinguish between correlation and causation. While a scatter plot may show a correlation between two variables, it does not necessarily mean that one variable causes the other.
4. Visualizing Scatter Plots
Guidelines
- Use clear and concise axis labels.
- Choose an appropriate scale for the axes.
- Consider using different colors, shapes, or sizes to distinguish different groups of data points.
Interactive Scatter Plots
Interactive scatter plots allow users to explore the data by hovering over points, zooming in and out, and changing the variables displayed.
5. Applications of Scatter Plots
Science
- Plotting the relationship between the concentration of a chemical and its reaction rate.
- Visualizing the relationship between the size of a plant and its yield.
Medicine
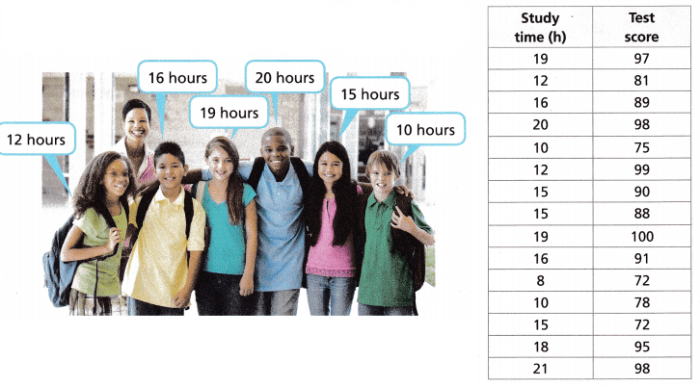
- Examining the relationship between a patient’s age and their risk of a particular disease.
- Assessing the correlation between the dosage of a drug and its effectiveness.
Business
- Analyzing the relationship between advertising expenditure and sales.
- Identifying the correlation between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty.
FAQs: Scatter Plots And Association Answer Key
What is a scatter plot?
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of data that uses dots to represent the values of two variables for each data point.
What is association in the context of scatter plots?
Association in scatter plots refers to the relationship between the two variables being plotted. It can be positive, negative, or nonexistent.
How can I identify outliers in a scatter plot?
Outliers are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data. They can be identified by their distance from the main cluster of points.